You are currently browsing the category archive for the ‘Skeletal’ category.
Skeletal System
#’s Axial, Apendendicular
Functions (6)
Histology
Haversion system + ______
5 things to identify
Cells (4)
(2) types of bones
Long bone – identify (9 items)
Composition : 1)______________
2) Matrix=____%
______%
Bone Ossification (2 types – which bones are made from thee?)
Where do all middle bones come from?
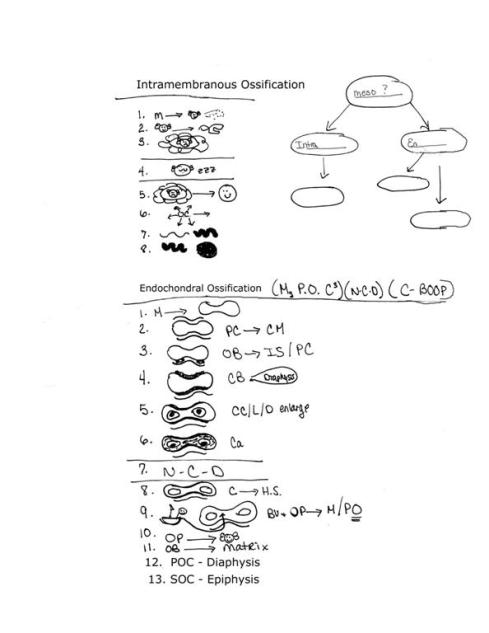
Intra_______ Ossification (8 steps)
Endochondral O_______ (13 steps)
Long bones increase length by…………………..
Diameter by……………..
Bones classified by? (4 – give examples)
2 other types.
What are the Growth Factors? (4) Give exact examples of each!
Where are the Paranasal Sinuses? What are the functions? Tissue?
What are Fontanels? Where are all 5 located and names?
Vertebral Column (#? Bones)
Draw and name curves.
Functions
What difference can you find between male/female bones?
Types of Fractures ( 8 )
Disorders (7)
CALCITONIN-
CANCELLOUS BONE-
COLLES FRACTURE-
COMMINUTED FRACTURE-
COMPOUND FRACTURE-
FONTANELS-
GREENSTICK FRACTURE-
INORGANIC SALTS-
KYPHOSIS-
LORDOSIS-
OBLIQUE FRACTURE-
ORGANIC FRAMEWORK-
OSTEOBLASTS/OSTEOCLASTS/OSTEOCYTES-
OSTEOMALACIA-
OSTEOMYELITIS-
OSTEONS –
OSTEOPOROSIS-
OSTEOPROGENITOR CELLS-
PARATHYROID-
POTT’S FRACTURE –
SCOLIOSIS-
SESAMOID-
SPIRAL FRACTURE –
THYROXINE-
TRANSVERSE FRACTURE –
WORMIAN-
Skeletal Questions
Can you name 5 fractures and describe?
What is the functions (6) of the curvature of the vertebral column?
What are the 4 curves of the vertebral and which is present at birth?
What are the Functions of the paranasal sinuses?
Describe the paranasal sinuses, and list 1 and it’s specific location.
What is a Fontanel?
What is the name of one Fontanel and what does it articulate with?
How do long bones increase in diameter by?
How do long bones increase in length by?
Name 4 minerals responsible for Growth and what the do.
What does thyroxine do?
What comes before “osteoblasts form bone matrix”, in endochondral ossification?
What are the types of ossification?
What comes after “trapped osteoblasts called osteocytes” in (other) ossification?
What bones are formed by endochondral ossification?
Both ossifications start from middle layer of___________ called __________.
Cartilage turns into bone. T F
What is the composition of bone? What constitutes the 33%, What constitutes the 67%
Name and draw the typical long bone, and identify at least 5 main points.
How is bone classified and name one bone for each.
Describe the two different Types of bone.
What are the functions of the Skeletal System? (6)
How many bones are in the appendicular?
What is the Histology of the Haversian system?
What is the difference between osteoprogenitor, osteoblast, osteocyte and osteoclast cells?
Most bones of the body
Bone formation preceded by cartilage model
Veiw Visual Step Chart to help memorize
Steps:
1. Mesenchyme cells form cartilage model
2. Perichondrium surrounds cartilage model
3. Osteoblasts differentiate on inner surface of perichondrium
4. Collar of compact bone surrounds cartilage model on diaphysis of model
5. Chondrocytes and lacunae in diaphysis enlarge (reducing amount of matrix)
6. Calcium deposits in remaining matrix (calcified cartilage)
7. Nutrients can’t diffuse
8. Chondrocytes die leaving hollow spaces
9. Blood vessels and osteoprogenitor cells enter matrix from periosteum
10. Osteoprogenitor cells differentiate into osteoblasts
11. Osteoblasts form bone matrix
12. This forms Primary Ossification Center in diaphysis
13. Secondary ossification center forms in epiphyses at time of birth or later
This includes the flat bones of the cranium, zygomatic, maxillae, mandible and part of the clavicles.
Veiw Visual Step Chart to help memorize
Steps:
1. Mesenchyme cells differentiate into osteoblasts and start to secrete matrix
2. Osteoblasts form spicules of matrix
3. Spicules trap osteoblasts in lacuna
4. Activity slows
5. Trapped osteoblasts called osteocytes
6. Bone growth proceeds outward from center (ossification center)
7. spicules thicken into trabeculae (spongy bone)
8. Trabeculae connect (compact bone)
Currently uploaded is the following worksheets (11) for Exam II
For Skeletal System (4): Skeletal Questions, Skeletal Volcabulary, Skeletal System. Ossification
For Arthrology (4): Arthrology Questions, Arthrology Volcabulary, Joints, Synovial Joints
For Muscular System (2) – Muscular Questions, Muscular Volcabulary
Functions Exam II
They should all be listed at the Left.
|
Skeletal System |
Support & Protection Movement Mineral Reservoir Hemopoiesis Energy Storage
|
|
Paranasal Sinuses |
Lighten Skull Warm Air Resonate Sound Protection Produce Mucus
|
|
Fontanels |
Allows for flexibility and skull growth
|
|
Vertebral Column Curves |
Increase strength, resilience, flexibility of spine, maintain balance, absorb shock, protect from fracture
|
|
Synovial Fluid |
Lubricates Nourishes Cushions/shock absorber
|
|
Muscles |
Body Movement Maintenance of posture Heat production Storage and movement of materials Support
|
|
|
|
Only current worksheets will be linked. The others will become available as we review their areas.
Exam worksheets are always available in SI, then the week of the exam, they will be available here.
Exam I Worksheets:


Feedback