You are currently browsing the category archive for the ‘Urinary’ category.
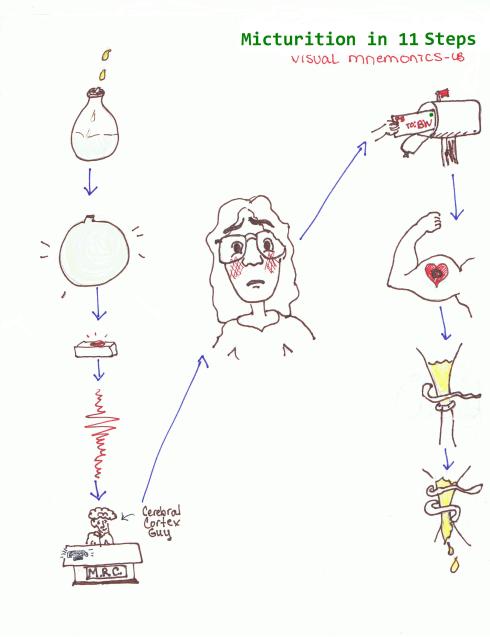
1. bladder fills with urine
2. walls stretch
3. stimulate stretch receptors
4. sensory impulses to spinal cord
5. relayed to cerebral cortex/micturation reflex center
6. Conscious desire to expel urine
7. parasympathetic impulses to bladder wall
8. detrusor muscle contracts
9. internal sphincter relaxes
10. external sphincter relaxed (voluntarily)
11. Micturition
Afferent arteriole –
Arcuate artery –
Calculi –
Cortex –
Cystitis –
Detrusor Muscle –
Diabetes Insipidus –
Distal convoluted tubule –
Dysuria –
Efferent arteriole –
External urethral sphincter –
Fibromuscular –
Globular Filtration –
Hematouria –
Homeostasis –
Hydrostatic –
Internal urethral sphincter –
Loop of Henle –
Medulla –
Micturition –
Nephritis –
Nephron –
Pelvis –
Penile –
Proximal convolute tubule –
Renal capsule –
Renal Failure –
Renal Reabsorption –
Renal Secretion –
Retroperitoneal –
Trigone –
Ureter –
Urethra –
Urethral orifice –
Describe the location of the kidneys anatomically.
Explain Renal Reabsorption.
Explain Renal Secretion.
What are the 11 steps of Micturition?
If you were blood, what would your path be starting at the Aorta, going to the Glomerulus?
If you were blood, what would your path be starting from the Kidney, going to the Renal Vein?
List 3 regions of the Kidney and what you would find there.
What 3 structures in the Urinary System would you find smooth muscle?
What are the functions of the Urinary System?
What disorder is when the bladder is inflamed?
What does a Nephron consist of?
What does the Distal Convoluted Tubule secrete?
What does the internal urethral sphincter do and what is its location?
What is Calculi?
What is another name for cessation of glomerular filtration?
What is Diabetes Insipidus?
What is the difference between Hematouria and Dysuria?
What is inflammation of the kidney called?
What is reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule?
What is the difference in length, and mucosa layers, of the male and female urethra?
What is the function of the ureter? The urethra?
What is the Histology of the following?
Glomerular capsule
Glomerulus Ureter
Urethra
Urinary Bladder
What is the Urinary System comprised of?
What order do these 3 processes happen: Reabsorption, Filtration, and Secretion?
What processes happens in the Nephrons?
|
Disorders |
Key |
(Descriptive) |
|
A. Bariatric Surgery |
A1 |
1. Gastric bypass, by narrowing/blocking portion of stomach |
|
B. Calculi |
|
2. Cavities in tooth enamel caused by plaque/bacteria |
|
C. Caries |
|
3. Frequent, watery feces |
|
D. Cystis |
|
4. Painful diarrhea caused by infectious organism |
|
E. Diabetes insipidus |
|
5. Dilated, tortuous veins around rectum/anus |
|
F. Diarrhea |
|
6. Viral infection of parotid glands |
|
G. Dysentery |
|
7. Inflammation of the pancreas |
|
H. Dysuria |
|
8. Painful urination |
|
I. Hematouria |
|
9. Blood in urine |
|
J. Hemorrhoids |
|
10. Bladder inflammation |
|
K. Mumps |
|
11. Stones in kidney |
|
L. Nephritis |
|
12. Inflammation of kidney |
|
M. Pancreatitis |
|
13. Not enough ADH produced by hypothalamus |
|
N. Renal Failure |
|
14. Cessation of glomerular filtration |
A1, B11, C2, D10, E13, F3, G4, H8, I9, J5, K6, L12, M7, N14
Only current worksheets will be linked. The others will become available as we review their areas.
Exam worksheets are always available in SI, then the week of the exam, they will be available here.
Exam I Worksheets:


Feedback